Abstract
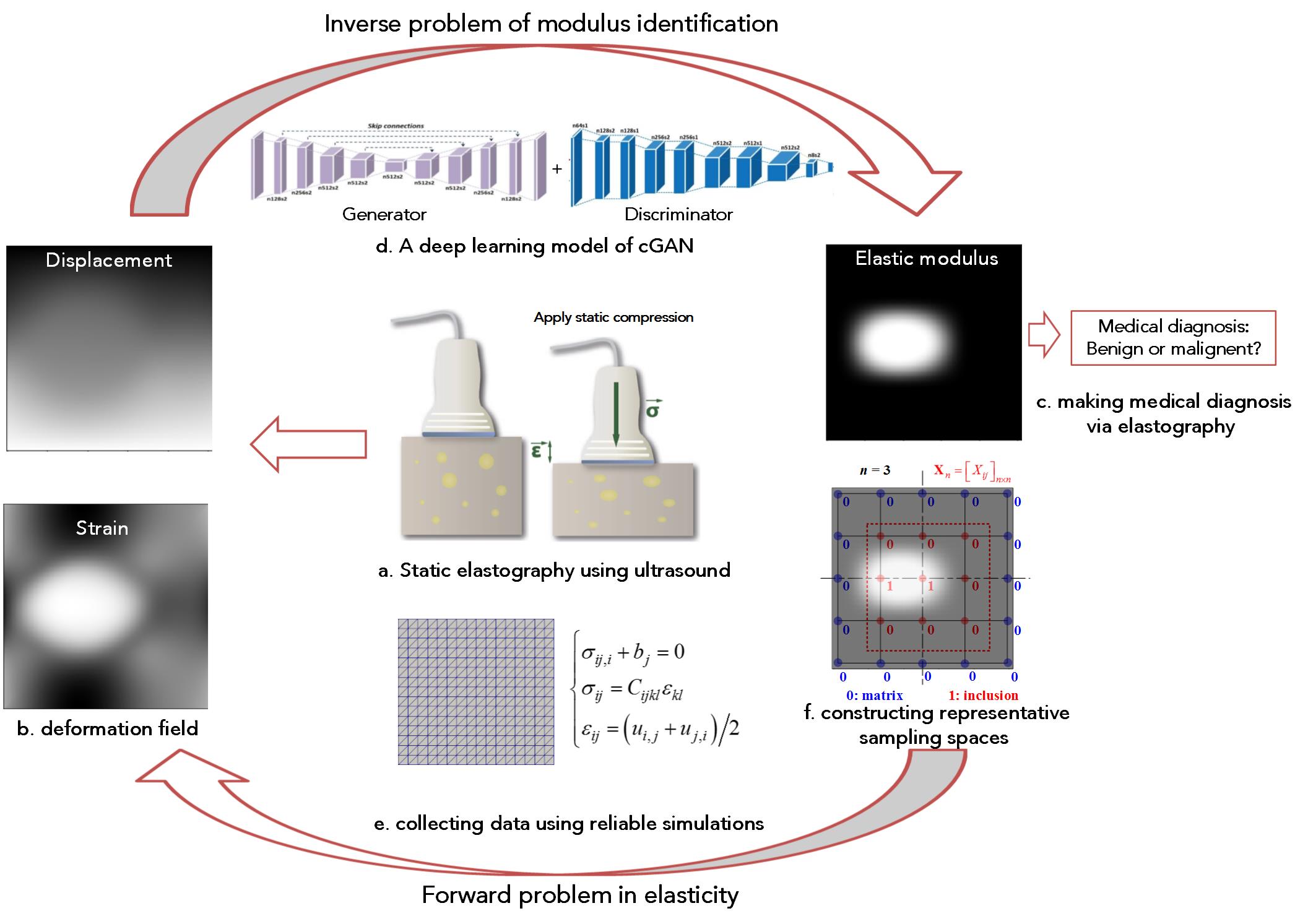
Non-destructive evaluation (NDE) of elastic modulus in materials has broad applications in fields such as geological exploration, quality evaluation and medical diagnosis. A key to these techniques is to solve the inverse problem of identifying the distribution of elastic modulus. While conventional theories and numerical methods often involve solving multiple variational problems iteratively for each individual case, the demand of real-time response and high-throughput application of NDE is growing, especially for advanced manufacturing and clinical practices. To address this challenge, in this letter, we leverage some of the recent progress in data science and propose a deep learning (DL) approach to solve the inverse problem of modulus identification in elasticity. By designing the sampling spaces of smooth distribution of shear modulus and adopting a conditional generative adversarial network (cGAN), we demonstrate that the DL approach can learn the high-dimensional mapping between distributions of strain and shear modulus via training over a limited portion of data. Also, the model can be rapidly deployed with high accuracy, bypassing the iterative solving process in the conventional methods. This work broadens the way of solving challenging inverse problems that aim for applications in real-time elastography and high-throughput NDE techniques.